ISO3601-4
ISO3601-4: Anti-extrusion rings (back-up rings)
ISO3601-4 defines tolerances and dimensions for five types of back-up rings (anti-extrusion rings):
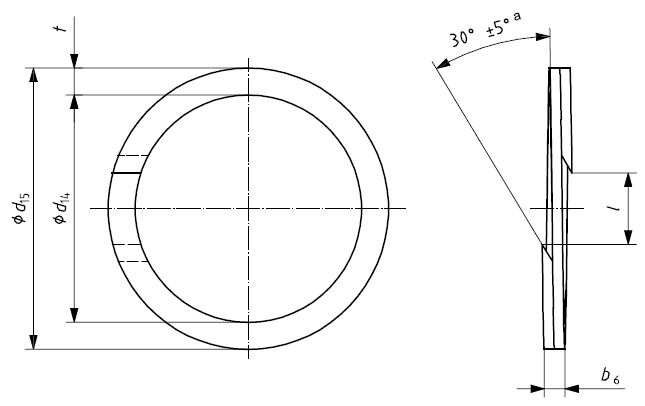
- (T1) – Spiral Type
- (T2) – Angle Cut Type
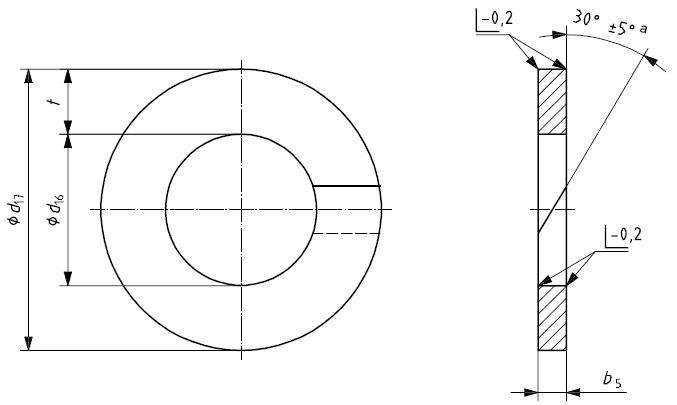
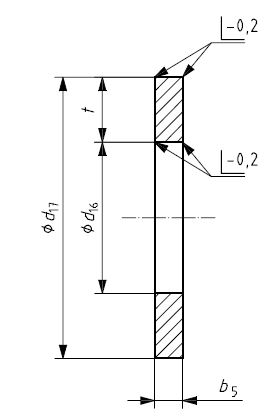
- (T3) – Solid Type
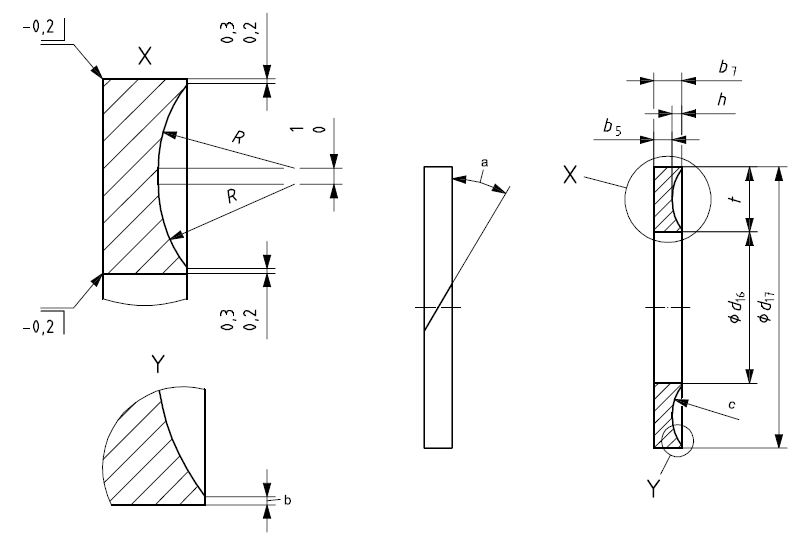
- (T4) – Angle Cut Concave Type
- (T5) – Solid Concave Type
These back-up rings are used with chosen O Ring sizes as defined in ISO3601-1 and the applicable housing dimensions defined in ISO3601-2.
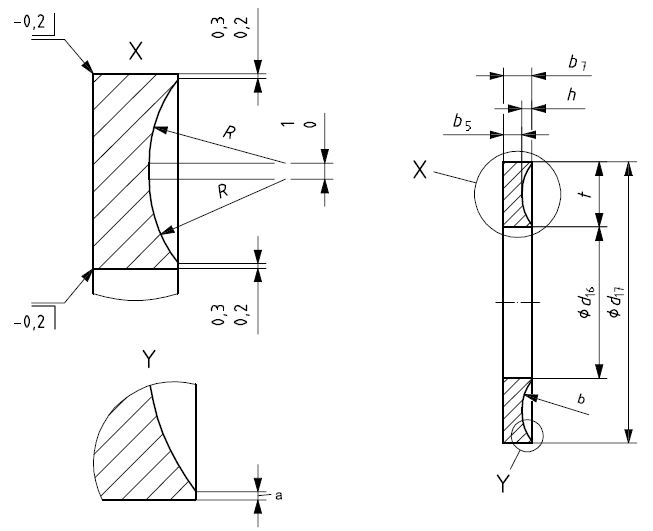
For general requirements of O Ring grooves, housing diameter tolerances, housing widths, surface roughness, lead-in chamfers, and edges and corners of undefined shape, please see ISO3601-2.
TYPES OF BACK-UP RINGS
Spiral Type T1
The Spiral Type is generally related to installations where the system pressures are between 10MPa (100 bar) and 20MPa (200 bar).
Connected rings, such as angle cut type or the solid type are favoured for use in stresses higher than 20MPa (200 bar), however, installation issues can be experienced with small diameters or closed grooves.
At raised temperatures, generally in excess of 100°C, back-up rings may be required even when the stress is lower than 100MPa (100 bar). Apart from pressure and temperature, particular operating circumstances may also demand the use of back-up rings. Operating media should be, therefore, considered and discussed between the customer and the manufacturer at the stage of design.
Angle Cut Type T2
The Angle Cut Type back-up rings are most extensively used, primarily because it is simpler to assemble than the solid type and presents better protection of the O Ring when the media pressure varies from 15MPa (150 bar) to beyond 20MPa (200 bar).
Solid Type T3
The solid Type back-up rings, although tough to assemble into O Ring grooves that are closed or have small diameters, presents supreme protection of the O Ring at all temperatures and pressures. It is a favoured type for temperatures higher than 135°C and system stresses larger than 25MPa (250 bar).
Angle Cut Concave Type T4
The Angle Cut Concave back-up rings are similar to the Angle Cut Type T2. The O ring will then preserve its shape under high stress. It is not suitable for automatic assemblies.
Solid Concave Type T5
The Solid Concave Type back-up rings are similar to the solid type T3, and produced to preserve its shape under high stress.
POSITIONING OF BACK-UP RINGS IN GROOVES
The positioning of back-up rings depends on the application and the direction in which stress acts on the O Ring groove.
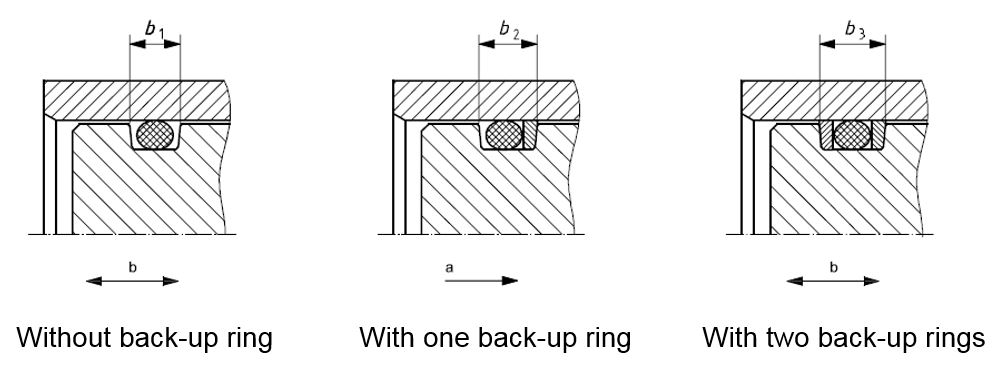
Back-up rings in a piston sealing application
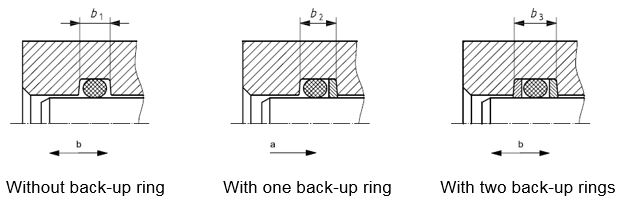
Back-up rings in a rod sealing application
MATERIALS
The most common material used for back-up rings is unfilled PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene). This is due to this material being very soft in comparison with other plastics. It shuts the extrusion gap under stress and guards the O Ring against extrusion into the gap between metal elements. For several assemblies, a portion of other materials may also be added to the PTFE in order to secure extra strength. These materials are generally: carbon (around 10% – 15% of the material mass), bronze (around 40% – 60%), and glass (around 15%).
For this type of installation Polyamide (PA) can also be used.
Hard/soft block Thermoplastics or Polyurethane (AU) are also used as long as they satisfy the purpose of preventing the O Ring from extruding into the gap between the metal elements under operating circumstances.
Click here to see the ISO3601 overview (Pt1, Pt2, Pt3, Pt4, Pt5).
If you require additional information about our range and/or services, download our catalogue or contact a member of the team.
E & OE. M Barnwell Services endeavour to make sure that all content is correct. Information has been gathered from manufacturing partners.